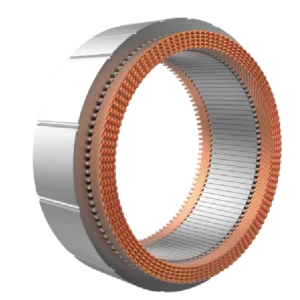
Advancements in motor technology often stem from refining fundamental components. One such innovation gaining traction is the use of flat wire windings in permanent magnet synchronous motors. This architectural shift from traditional round wires represents a substantive engineering change with measurable impacts on the core characteristics of a pmsm motor.
The Principle of Enhanced Copper Fill
The primary advantage of flat wire, or rectangular wire, lies in its geometric efficiency. In a standard electric motor stator, circular copper wires leave inevitable air gaps when wound, resulting in a lower copper fill factor. Flat wire windings, by contrast, pack together more efficiently, similar to stacking books instead of placing round pipes in a box. This allows for a significantly higher volume of conductive copper within the same stator slot. A higher copper fill directly reduces the resistance in the windings. For a pmsm motor, this translates into lower I²R losses, which is a primary source of heat and energy waste, leading to a direct improvement in electrical efficiency.
Thermal and Power Density Implications
The benefits of reduced resistance extend into thermal management. With lower copper losses, the electric motor generates less intrinsic heat under the same load conditions. This allows the motor to deliver more continuous power without reaching critical temperatures or, alternatively, to be downsized for the same power output. Furthermore, the flat surface area of the conductors can improve heat conduction from the inside of the winding to the stator core, which acts as a heat sink. This enhanced thermal performance is crucial for a pmsm motor operating in demanding duty cycles, as it supports higher overload capability and improves long-term reliability by reducing thermal stress on insulation materials.
Impact on High-Speed Performance and Durability
The rigid structure of pre-formed flat wire windings also offers mechanical advantages. The entire winding assembly possesses greater structural integrity, which better resists the electromagnetic forces and vibrations experienced at high rotational speeds. This increased mechanical robustness can minimize the risk of insulation abrasion and short circuits over the motor’s operational life. However, it is important to note that at very high frequencies, skin and proximity effects—where current crowds toward the conductor surface—can become more pronounced in large flat conductors. This requires careful design regarding the specific dimensions of the flat wire to optimize performance across the intended speed range of the pmsm motor.
The integration of flat wire windings is a definitive step toward maximizing the inherent performance of permanent magnet synchronous motor technology. It is a design choice that directly addresses key limitations of efficiency, thermal capacity, and power density. For applications where these parameters are critical, specifying a Santroll PMSM motor that utilizes flat wire construction can yield tangible gains in system performance and operational cost. This approach reflects Santroll’s continuous pursuit of refinement in electric motor architecture, pushing the boundaries of what is electrically and mechanically possible.